|
|
Partnership for Advanced Computing in Europe (PRACE)
PRACE Award N.2012060993
Filling the gap between supernova explosions and their remnants:
the Cassiopeia A laboratory
Orlando S., Bocchino F., Miceli M., Pumo M.L., Reale F., Peres G.
2012/2013
|
Supernova remnats (SNRs) show a complex morphology characterized
by a complex spatial distribution of ejecta, believed to reflect
pristine structures and features of the progenitor supernova (SN)
explosion. Filling the gap between SN explosions and their remnants
is very important in Astrophysics for a comprehension of the origin
of present-day structure of ejecta in SNRs and to probe and constraint
current models of SN explosions. A detailed model connecting the
SN explosion with the SNR evolution is presently missing.
|
|
The aim of this project is to study the ejecta dynamics from the
immediate aftermath of the SN explosion to their expansion in the
SNR with unprecedented model resolution and completeness to answer,
for the first time, important questions as: how does the final
remnant morphology reflects the characteristics of the ejecta formed
in the aftermath of the SN explosion?
Since the SNR Cassiopeia A (Cas A) is an attractive laboratory for
studying the SNe-SNRs connection (being one of the best studied
SNRs for which its 3D structure is known), our model describes its
evolution with complete and realistic conditions of the initial
ejecta structure. The plasma evolution is described by solving the
full 3D hydrodynamic plasma equations. The finer ejecta features
are described with unprecedented spatial resolution (down to 8.8e11
cm) at a level of detail not feasible before.
Our project is based on a single large-scale 3D hydrodynamic simulation. The
initial ejecta structure will be derived by a model of the "early"
post-explosion evolution (from the breakout of the shock wave at
the stellar surface up to the so-called nebular stage) of core-collapse
SNe, taking into account the constraints on the spatial distribution
of ejecta derived from observations. The initial remnant is modelled
as a sphere centered on the origin of the Cartesian coordinate
system with radius R = 1400 Rsun (~ 3e-5 pc; corresponding to an
initial age of ~ 31 hrs after the SN explosion). We follow the SNR
evolution for 330 yr (namely the age of Cas A).
The calculations were performed using FLASH, an adaptive mesh
refinement multiphysics code for astrophysical plasmas. The
hydrodynamic equations for compressible gas dynamics are solved
using the FLASH implementation of the piecewice-parabolic method.
A major challenge in modelling the SN explosion of Cas A is the
very small scale of the SN at early stages compared with the size
of the rapidly expanding blast wave. The initial remnant is modelled
as a sphere centered on the origin of the Cartesian coordinate
system with radius R = 1400 Rsun (~ 3e-5 pc; corresponding to an
initial age of ~ 31 hrs after the SN explosion). We follow the SNR
evolution for 330 yr (namely the age of Cas A) when its final radius
is ~ 2.5 pc. To capture this enormous range of scales, the model
explored here employed 20 nested levels of adaptive mesh refinement,
with resolution increasing twice at each refinement level. This
grid configuration yields an effective resolution of ~ 13 Rsun at
the finest level, corresponding to ~ 100 grid points per initial
radius of the blast.
|
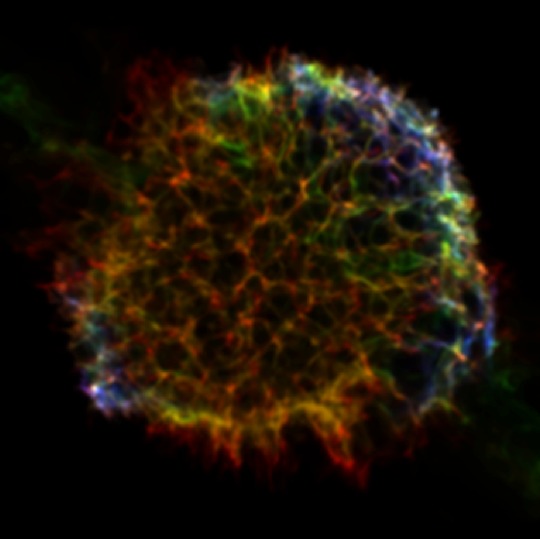
|
3D volumetric rendering of plasma density with temperature
above 1 MK for a test model with a mass of ejecta 4.2 Msun and
energy 2.3 foe. Each color represents the ejecta material rich
of Ne and O (red), Ar and Si (green), and Fe and Ni (blue). The
final radius of the remnant is 2.5 pc in nice agreement
with the observations.
[Clik on the figure to enlarge] |
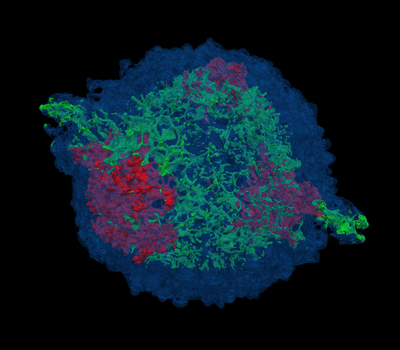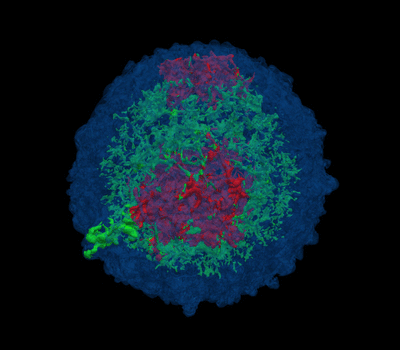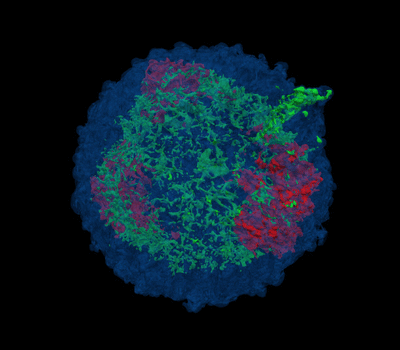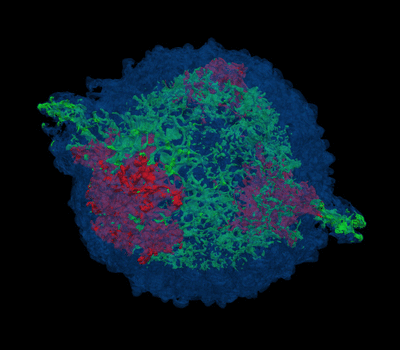
|
3D view of plasma density with temperature
above 1 MK for a test model with a mass of ejecta 4.2 Msun and energy
2.3 foe. Each color represents the ejecta material rich of Ar and Si
(green), and Fe and Ni (red). The shocked ISM is highlighted in blue.
|
|
Selected movies
 |
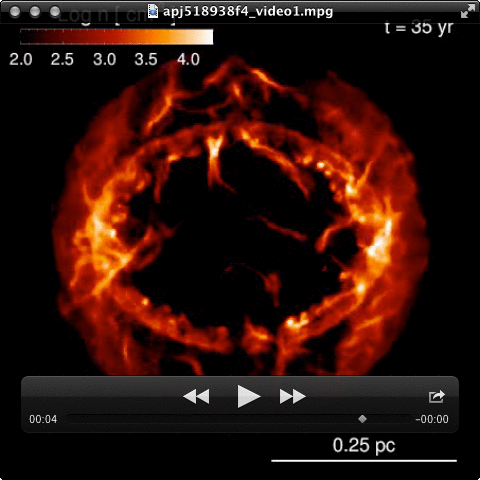 |
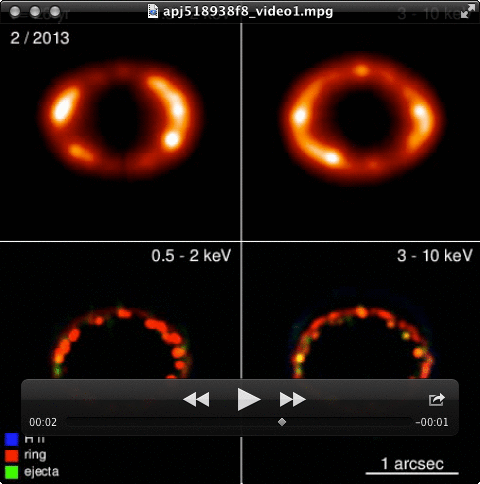
Density evolution of SN 1987A (left) and corresponding evolution of X-ray emission (right).
(Orlando S., Miceli M., Pumo M.L., Bocchino F. 2015, ApJ 810, 168)
 |
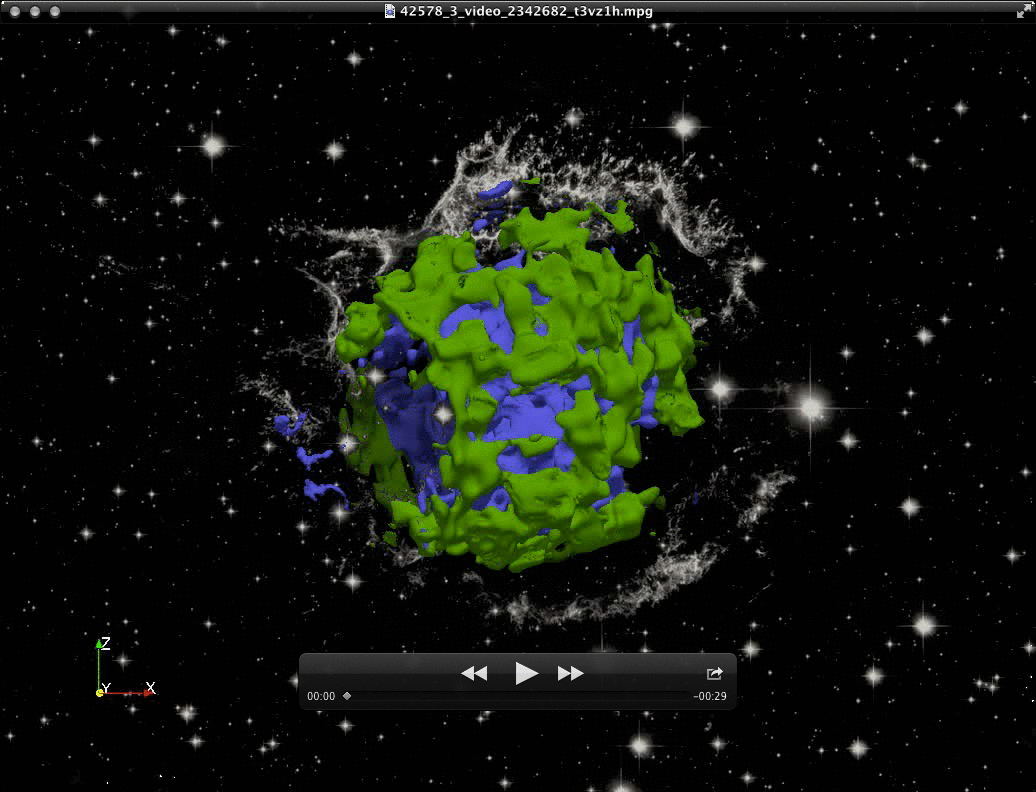 |
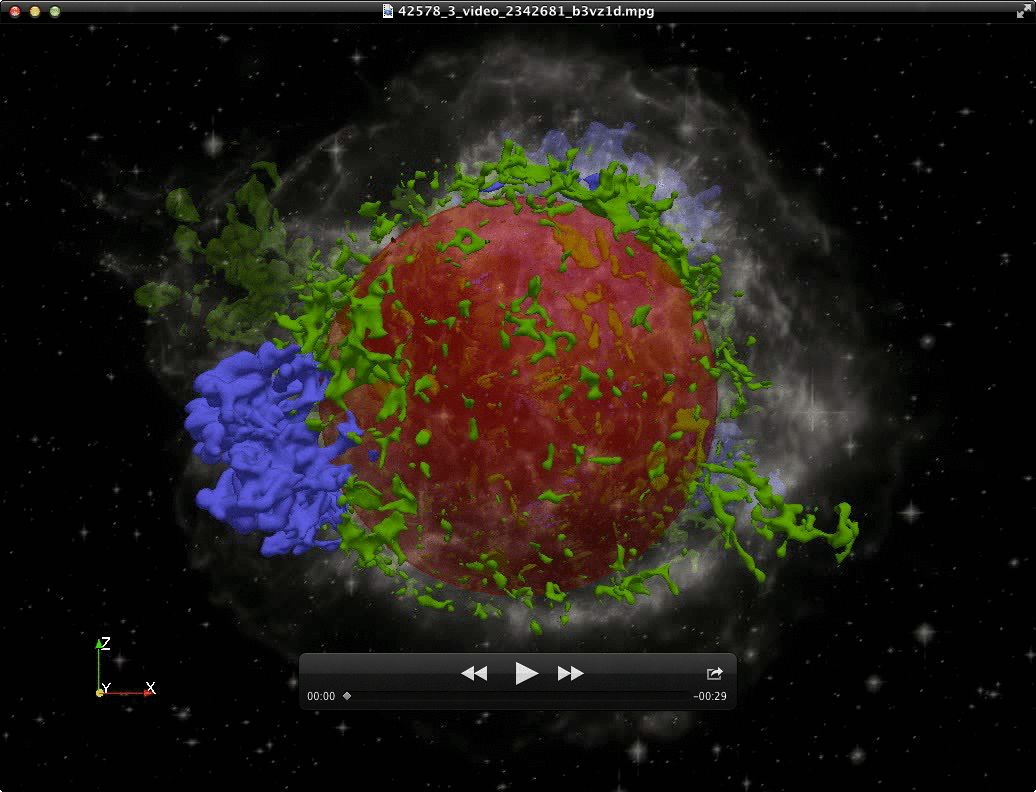
Spatial distribution of shoched (left) and unshocked (right) ejecta in
SNR Cassiopeia A; iron-rich ejecta are in blue, silicon/sulfur-rich ejecta
in green; the red sphere marks the nominal position of reverse shock.
(Orlando S., Miceli M., Pumo M.L., Bocchino F. 2016, ApJ 822, id. 22)
Video on YouTube: A journey around Supernova 1987A
The results have been published in peer-reviewed international journals
and presented at international meetings.
Refereed publications
-
Collisionless shock heating of heavy ions
in SN 1987A
Miceli M., Orlando S., Burrows D.N.,
Frank K.A., Argiroffi C., Reale F., Peres G., Petruk O., Bocchino F.
2019, Nature Astronomy 3, 236
(ADS link)
-
Linking gamma-ray spectra of supernova
remnants to the cosmic ray injection properties in the aftermath
of supernovae
Petruk O., Orlando S., Miceli M.,
Bocchino F. 2017, A&A 605, A110
(ADS link)
-
Modeling SNR Cassiopeia A from the
Supernova Explosion to its Current Age: The role of post-explosion
anisotropies of ejecta
Orlando S., Miceli M., Pumo
M.L., Bocchino F. 2016, ApJ 822, id. 22
(ADS link)
-
Supernova 1987A: a Template to Link
Supernovae to Their Remnants
Orlando S., Miceli M.,
Pumo M.L., Bocchino F. 2015, ApJ 810, 168
(ADS link)
Invited presentations
-
Connecting Supernova Remnants to their
progenitor SN explosions: the Cassiopeia A and SN 1987A laboratories
Orlando S. 2017, invited talk at the
workshop "The Progenitor-Supernova-Remnant Connection",
Ringberg Castle, Germany, 24-28 July 2017
-
Modeling the SNR Cassiopeia A from the
immediate aftermath of the SN explosion to the full development of
its remnant
Orlando S. 2017, invited talk at the
workshop "CSI: Princeton - A Definitive Investigation of the
Core-Collapse Supernova Cassiopeia A", Princeton Center for
Theoretical Science, Princeton, USA, 17-19 April 2017
-
Bridging the gap between SNe
and their remnants through multi-dimensional hydrodynamic
modeling
Orlando S., Miceli M., Petruk O. 2017,
invited talk at IAU Symposium 331, "SN 1987A, 30 years later -
Cosmic Rays and Nuclei from Supernovae and their aftermaths",
La Reunion Island, France, 20-24 February 2017
Talk/poster contributions to international meetings
-
The supernova - supernova remnant
connection through multi-dimensional magnetohydrodynamic modeling
Orlando S., Miceli M., Petruk O., Ono M., Nagataki
S., Peres G., Bocchino F. 2017, contributed talk at the workshop
"The X-ray Universe 2017", Rome, Italy, 6-9 June 2017.
-
The physical origin of the X-ray emission
from SN 1987A
Miceli M., Orlando S., Petruk O.,
Argiroffi C., Bocchino F. 2017, contributed talk at the workshop
"The X-ray Universe 2017", Rome, Italy, 6-9 June 2017.
-
Investigating the origin of the X-ray
emission from SN 1987A
Miceli M., Orlando S.,
Petruk O., Argiroffi C., Bocchino F. 2017, contributed talk at IAU
Symposium 331, "SN 1987A, 30 years later - Cosmic Rays and Nuclei
from Supernovae and their aftermaths", La Reunion Island, France,
20-24 February 2017
-
Linking SNe and SNRs. Time-dependent
injection in SN 1987A and gamma-ray emission of IC 443
Petruk O., Orlando S., Miceli M., Bocchino F. 2017,
contributed talk at IAU Symposium 331, "SN 1987A, 30 years later
- Cosmic Rays and Nuclei from Supernovae and their aftermaths",
La Reunion Island, France, 20-24 February 2017
-
Modeling post-explosion anisotropies of
ejecta in SNR Cassiopeia A
Orlando S., Miceli M.,
Pumo M.L., Bocchino F. 2016, contributed talk at the conference
"Supernova Remnants: An Odyssey in Space after Stellar Death"
Crete, Greece, 6-11 June 2016
(ADS link)
-
Three-dimensional hydrodynamic modeling
of SN 1987A from the supernova explosion till the Athena
era
Orlando S., Miceli M., Pumo M.L., Bocchino
F. 2016, poster presented at the conference "Supernova Remnants: An
Odyssey in Space after Stellar Death" Crete, Greece, 6-11 June 2016
(ADS link)
-
Modeling post-explosion anisotropies of
ejecta in SNR Cassiopeia A
Orlando S., Miceli M.,
Pumo M.L., Bocchino F. 2016, poster presented at the conference
"XMM-Newton: The Next Decade", ESAC, Madrid, Spain, 9-11 May 2016
(ADS link)
-
3D Hydrodynamic Modeling of SN 1987A from
the SN explosion till the Athena Era
Orlando S.,
Miceli M., Pumo M.L., Bocchino F. 2015, poster presented at the
conference "Exploring the Hot and Energetic Universe: The first
scientific conference dedicated to the Athena X-ray observatory",
Madrid, Spain, 8-10 September, 2015
(ADS link)
-
HPC Projects in Astrophysics at INAF/OAPA:
Current Challenges and Future Perspectives
Orlando
S. 2014, contributed talk at the ICT Meeting, Cagliari, Italy,
Sept. 2014
-
3D hydrodynamic modeling of SN 1987A:
from the supernova explosion till the Athena era
Orlando S., Miceli M., Pumo M.L., Bocchino F. 2014, contributed talk
at the meeting "The X-ray Universe 2014", Trinity College Dublin,
Ireland, 16-19 June 2014
(ADS link)
-
Filling the gap between
supernova explosions and their remnants: the Cassiopeia A
laboratory
Orlando S., Miceli M., Pumo M.L.,
Bocchino F., Reale F., Peres G. 2014, poster presented at the meeting
"The X-ray Universe 2014", Trinity College Dublin, Ireland, 16-19
June 2014
(ADS link)
-
HPC Projects in Astrophysics at OAPA/UNIPA:
Current Challenges and Future Perspectives
Orlando
S., contributed talk at the CINECA-UNIPA meeting, Palermo, Italy,
May 2014
-
HPC projects in Astrophysics at INAF/OAPa:
current challenges and future perspectives
Orlando
S., contributed talk at the PRACE-2IP WP8 Fifth Face to Face Meeting
CSCS, Lugano, Switzerland, 6-8/03/2013;
Press release
-
Press release on Media Inaf (January
2019), "Shock senza collisioni per la supernova 1987A"
(more)
-
NASA/Chandra: Interview at S. Orlando
(February 2017)
(more)
-
Italian Space Agency: Press release
(February 2017), "Trenta candeline per SN 1987A"
(more)
-
Press release on Media Inaf
(February 2017), "Buon compleanno 1987A!" (more)
-
Press release on Media Inaf (September
2015), "Un modello 3D per la supernova 1987A" (more)
Web and Media
-
NASA: printable 3D model of SN 1987A (April 2017)
(more)
-
NASA (February 2017)
(more)
-
NASA/Hubble (February 2017)
(more)
-
NASA/Chandra (February 2017)
(more)
-
NRAO (February 2017)
(more)
-
PHYS.ORG (February 2017)
(more)
-
Astronomy Magazine (February 2017)
(more)
-
Cosmos Magazine (February 2017)
(more)
-
Universe Today (February 2017)
(more)
|
|
|
|